General Information
-
DRAMP ID
- DRAMP00133
-
Peptide Name
- Lactococcin G subunit beta (Gbeta ; Bacteriocin)
-
Source
- Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis (Streptococcus lactis) (Gram-positive bacteria)
-
Family
- Belongs to the class IIb bacteriocin
-
Gene
- Not found
-
Sequence
- KKWGWLAWVDPAYEFIKGFGKGAIKEGNKDKWKNI
-
Sequence Length
- 35
-
UniProt Entry
- P36962
-
Protein Existence
- Protein level
Activity Information
-
Biological Activity
- Antimicrobial, Antibacterial
-
Target Organism
- Lactococcus.
-
Hemolytic Activity
-
- No hemolysis information or data found in the reference(s) presented in this entry
-
Cytotoxicity
-
- Not included yet
-
Binding Target
- Not found
Structure Information
-
Linear/Cyclic
- Not included yet
-
N-terminal Modification
- Not included yet
-
C-terminal Modification
- Not included yet
-
Nonterminal Modifications and Unusual Amino Acids
- Not included yet
-
Stereochemistry
- Not included yet
-
Structure
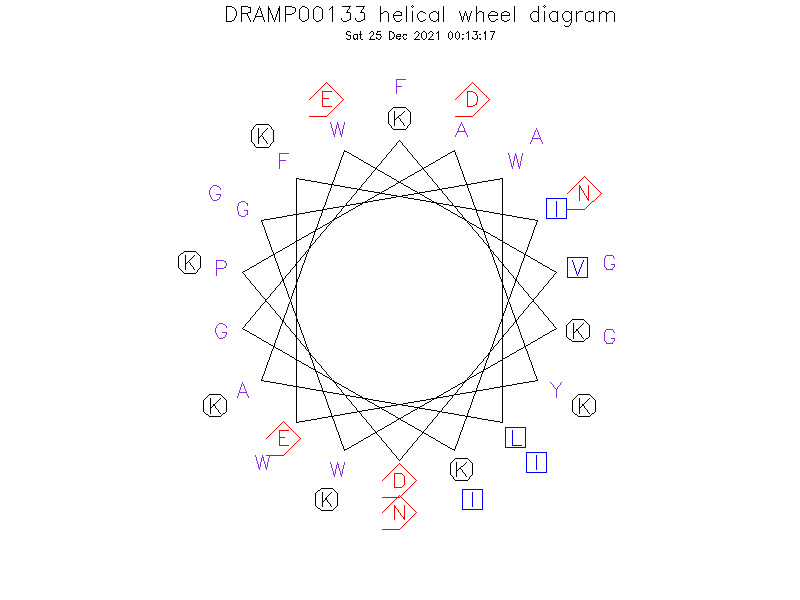
- Alpha helix
-
Structure Description
- In DPC, LcnG-beta has an N-terminal alpha-helix (residues 6-19). The region from residues 20 to 35, which also contains a flexible GxxxG-motif (residues 18-22), appeared to be fairly unstructured in DPC.
-
Helical Wheel Diagram
- 2JPK->
-
Predicted Structure
- There is no predicted structure for DRAMP00133.
Physicochemical Information
-
Formula
- C198H291N49O47
Absent Amino Acids
- CHMQRST
Common Amino Acids
- K
Mass
- 4109.79
PI
- 9.7
Basic Residues
- 8
Acidic Residues
- 4
Hydrophobic Residues
- 14
Net Charge
- +4
-
Boman Index
- -39.75
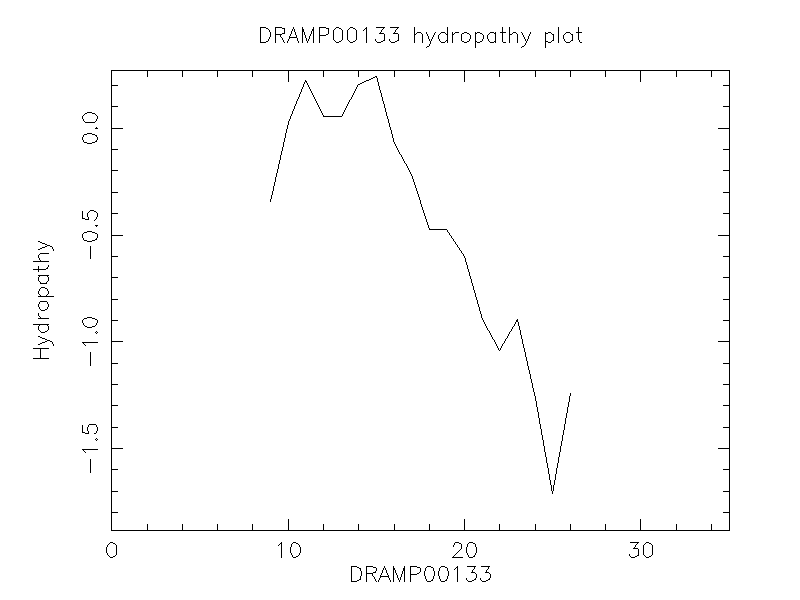
Hydrophobicity
- -0.806
Aliphatic Index
- 61.43
Half Life
-
- Mammalian:1.3 hour
- Yeast:3 min
- E.coli:2 min
Extinction Coefficient Cystines
- 23490
Absorbance 280nm
- 690.88
Polar Residues
- 8
DRAMP00133
Comments Information
MOA
- The N-terminal halves of both the alpha and beta peptides may form amphiphilic alpha-helices, suggesting that the peptides are pore-forming toxins that create cell membrane channels through a "barrel-stave" mechanism. Bacteriocin activity requires interaction of alpha and beta peptides in a molar ratio of 7
Literature Information
- ·Literature 1
-
Title
- A novel lactococcal bacteriocin whose activity depends on the complementary action of two peptides.
-
Pubmed ID
- 1512201
-
Reference
- J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(17):5686-5692.
-
Author
- Nissen-Meyer J, Holo H, H¥varstein LS, Sletten K, Nes IF.
- ·Literature 2
-
Title
- Three-dimensional structure of the two peptides that constitute the two-peptide bacteriocin lactococcin G.
-
Pubmed ID
- 18187052
-
Reference
- Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Mar;1784(3):543-554.
-
Author
- Rogne P, Fimland G, Nissen-Meyer J, Kristiansen PE.