General Information
-
DRAMP ID
- DRAMP01549
-
Peptide Name
- Caerin-1.1 (Frogs, amphibians, animals)
-
Source
- Litoria splendida (Magnificent tree frog) (Litoria gilleni) (Litoria caerulea)
-
Family
- Belongs to the frog skin active peptide family (Caerin subfamily)
-
Gene
- Not found
-
Sequence
- GLLSVLGSVAKHVLPHVVPVIAEHL
-
Sequence Length
- 25
-
Protein Existence
- Protein level
Activity Information
-
Biological Activity
- Antimicrobial, Antibacterial, Anti-Gram+, Anti-Gram-, Antiviral
-
Target Organism
-
- [Ref.15203252]Gram-positive bacteria: Bacillus cereus (MIC=50 µg/ml), Leuconostoc lactis (MIC=1.5 µg/ml), Listeria innocua (MIC=25 µg/ml), Micrococcus luteus (MIC=12.5 µg/ml), Staphylococcus aureus (MIC=3-12 µg/ml), Staphylococcus epidermis (MIC=12.5 µg/ml), Streptococcus uberis (MIC=12.5 µg/ml);
- Gram-negative bacterium: Pasteurella multocida (MIC=25 µg/ml).
- [Ref.16140737]Virus:HIV:inhibit 50% of PBS-treated HIV infection of T cells(IC50=7.8 μM);inhibition of HIV transfer by dendritic cells to T cells(IC50=12.6 μM)
-
Hemolytic Activity
-
- No hemolysis information or data found in the reference(s) presented in this entry
-
Cytotoxicity
- No cytotoxicity information found in the reference(s) presented
-
Binding Target
- Cell membrane
Structure Information
-
Linear/Cyclic
- Linear
-
N-terminal Modification
- Free
-
C-terminal Modification
- Amidation
-
Nonterminal Modifications and Unusual Amino Acids
- Free
-
Stereochemistry
- L
-
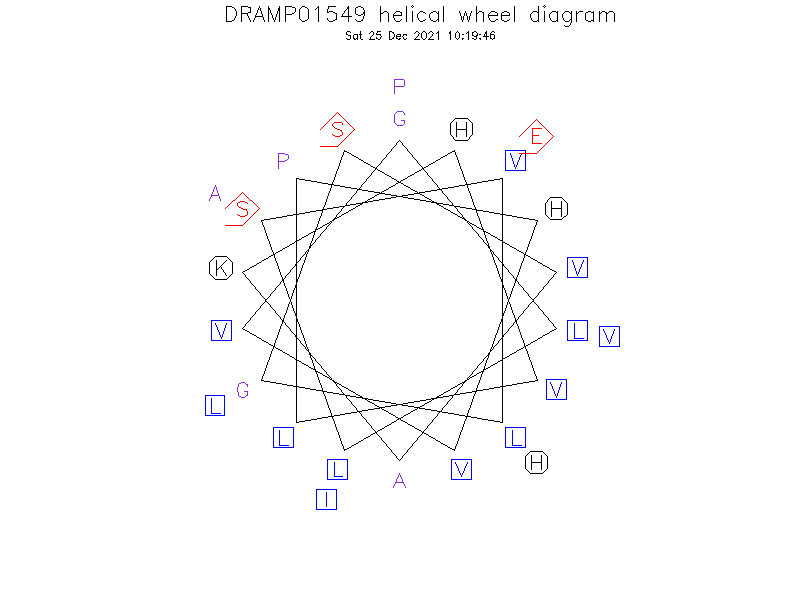
Structure
- Alpha helix
-
Structure Description
- The peptide adopts two well-defined helices from Leu2 to Lys11 and from Val17 to His24 separated by a region of less-defined helicity and greater flexibility.
-
Helical Wheel Diagram
-
PDB ID
- None
-
Predicted Structure
- There is no predicted structure for DRAMP01549.
Physicochemical Information
-
Formula
- C121H202N32O30
Absent Amino Acids
- CDFMNQRTWY
Common Amino Acids
- V
Mass
- 2585.13
PI
- 7.02
Basic Residues
- 4
Acidic Residues
- 1
Hydrophobic Residues
- 14
Net Charge
- +3
-
Boman Index
- 26.12
Hydrophobicity
- 1.188
Aliphatic Index
- 171.2
Half Life
-
- Mammalian:30 hour
- Yeast:>20 hour
- E.coli:>10 hour
Extinction Coefficient Cystines
- 0
Absorbance 280nm
- 0
Polar Residues
- 4
DRAMP01549
Comments Information
Function
- Antibacterial and antiviral peptides that adopt an alpha helical conformation which can disrupt bacterial membranes. Each caerin displays a different antimicrobial specificity.
Tissue specificity
- Secreted by the skin parotoid and/or rostral glands.
Domain
- Contains two amphipathic alpha helix regions separated by a region of less-defined helicity and greater flexibility.
Miscellaneous
- Caerin 1.1 completely inhibits HIV infection of T cells within minutes of exposure to virus at concentrations that were not toxic to target cells (J Virol. 2005 Sep;79(18)
PTM
- C-terminal amidation.
Literature Information
- ·Literature 1
-
Title
- Antimicrobial peptides from amphibian skin potently inhibit human immunodeficiency virus infection and transfer of virus from dendritic cells to T cells.
-
Pubmed ID
- 16140737
-
Reference
- J Virol. 2005 Sep;79(18):11598-606.
-
Author
- VanCompernolle SE, Taylor RJ, Oswald-Richter K, Jiang J, Youree BE, Bowie JH, Tyler MJ, Conlon JM, Wade D, Aiken C, Dermody TS, KewalRamani VN, Rollins-Smith LA, Unutmaz D.
- ·Literature 2
-
Title
- The solution structure and activity of caerin 1.1, an antimicrobial peptide from the Australian green tree frog, Litoria splendida.
-
Pubmed ID
- 9266696
-
Reference
- Eur J Biochem. 1997 Jul 15;247(2):545-557.
-
Author
- Wong H, Bowie JH, Carver JA.
- ·Literature 3
-
Title
- Antimicrobial peptides from hylid and ranin frogs originated from a 150-million-year-old ancestral precursor with a conserved signal peptide but a hypermutable antimicrobial domain.
-
Pubmed ID
- 12709067
-
Reference
- Eur J Biochem. 2003 May;270(9):2068-2081.
-
Author
- Vanhoye D, Bruston F, Nicolas P, Amiche M.
- ·Literature 4
-
Title
- Host-defence peptides of Australian anurans: structure, mechanism of action and evolutionary significance.
-
Pubmed ID
- 15203252
-
Reference
- Peptides. 2004 Jun;25(6):1035-1054.
-
Author
- Apponyi MA, Pukala TL, Brinkworth CS, Maselli VM, Bowie JH, Tyler MJ, Booker GW, Wallace JC, Carver JA, Separovic F, Doyle J, Llewellyn LE.