General Information
-
DRAMP ID
- DRAMP00170
-
Peptide Name
- Carnocyclin A (CclA; Bacteriocin)
-
Source
- Carnobacterium maltaromaticum UAL307 (Gram-positive bacteria)
-
Family
- Belongs to the class IIc bacteriocin
-
Gene
- cclA
-
Sequence
- LVAYGIAQGTAEKVVSLINAGLTVGSIISILGGVTVGLSGVFTAVKAAIAKQGIKKAIQL
-
Sequence Length
- 60
-
UniProt Entry
- B2MVM5
-
Protein Existence
- Protein level
Activity Information
-
Biological Activity
- Antimicrobial, Antibacterial, Anti-Gram+
-
Target Organism
-
- Gram-positive bacteria: Carnobacterium maltaromaticum UAL26, C. maltaromaticum LV17A, C. divergens LV13, Brochothrix campestris ATCC 43754, B. thermosphacta ATCC 11509, Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 7080, E. faecium ATCC 19434, E. faecium BFE900, Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis ATCC 11454, Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris ATCC 11602, Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis DPC3147, Lactobacillus sakeii 706, L. sakei UAL1218, Leuconostoc mesenteroides Y105, Pediococcus acidilactici PAC1.0, Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 15313, Listeria monocytogenes H7762, Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 43256, Listeria monocytogenes HPB 642, Listeria monocytogenes UAFM 1, Listeria monocytogenes UAFM 15, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213.
-
Hemolytic Activity
-
- No hemolysis information or data found in the reference(s) presented in this entry
-
Cytotoxicity
- No cytotoxicity information found in the reference(s) presented
-
Binding Target
- Lipid II
Structure Information
-
Linear/Cyclic
- Cyclic
-
N-terminal Modification
- No specific N-terminal
-
C-terminal Modification
- No specific C-terminal
-
Nonterminal Modifications and Unusual Amino Acids
- None
-
Stereochemistry
- L
-
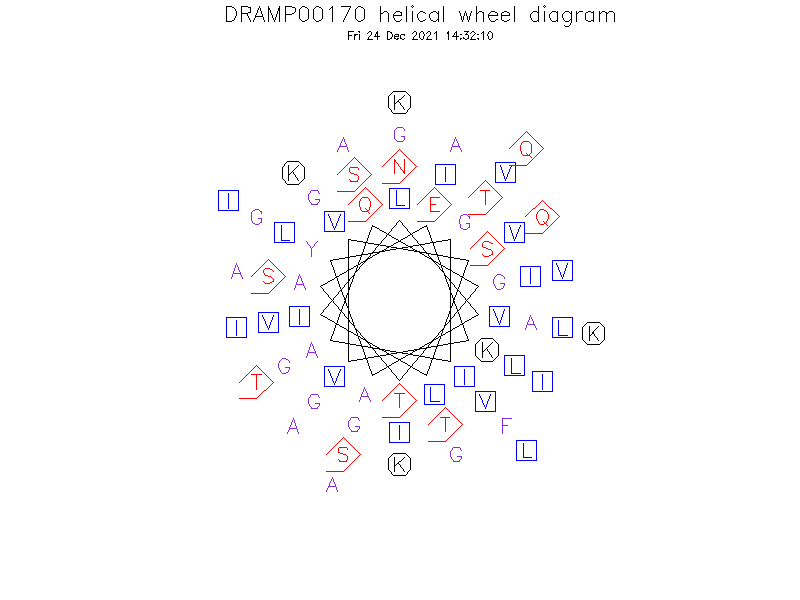
Structure
- Alpha helix (4 helices; 38 residues)
-
Structure Description
- The NMR study results reveal that CclA preferentially binds halide anions and has a structure that is surprisingly similar to that of AS-48 despite low sequence identity, different oligomeric state, and disparate function. CclA folds into a compact globular bundle, comprised of four helices surrounding a hydrophobic core.
-
Helical Wheel Diagram
-
PDB ID
- 2KJF resolved by NMR.
-
Predicted Structure
- There is no predicted structure for DRAMP00170.
Physicochemical Information
-
Formula
- C269H463N69O76
Absent Amino Acids
- CDHMPRW
Common Amino Acids
- AGIV
Mass
- 5880.05
PI
- 10
Basic Residues
- 5
Acidic Residues
- 1
Hydrophobic Residues
- 32
Net Charge
- +4
-
Boman Index
- 47.09
Hydrophobicity
- 1.058
Aliphatic Index
- 144.67
Half Life
-
- Mammalian:5.5 hour
- Yeast:3 min
- E.coli:2 min
Extinction Coefficient Cystines
- 1490
Absorbance 280nm
- 25.25
Polar Residues
- 19
DRAMP00170
Comments Information
Function
- Carnocyclin A (CclA) is a potent antimicrobial peptide from Carnobacterium maltaromaticum UAL307 that displays a broad spectrum of activity against numerous Gram-positive organisms.
Biophysicochemical properties
- pH dependence (Stable from pH 2 to 12); Temperature dependence (Displays a high degree of stability when incubated at temperatures between -80 and 75 degrees Celsius for 60 minutes. Autoclaving the peptide at 121 degrees Celsius for 15 minutes had no effect but incubation at 100 degrees Celsius for 60 minutes caused a 32-fold reduction in activity).
Literature Information
- ·Literature 1
-
Title
- Isolation and characterization of carnocyclin a, a novel circular bacteriocin produced by Carnobacterium maltaromaticum UAL307.
-
Pubmed ID
- 18552180
-
Reference
- Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008 Aug;74(15):4756-4763.
-
Author
- Martin-Visscher LA, van Belkum MJ, Garneau-Tsodikova S, Whittal RM, Zheng J, McMullen LM, Vederas JC.
- ·Literature 2
-
Title
- The three-dimensional structure of carnocyclin A reveals that many circular bacteriocins share a common structural motif.
-
Pubmed ID
- 19692336
-
Reference
- J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 16;284(42):28674-81.
-
Author
- Martin-Visscher LA, Gong X, Duszyk M, Vederas JC.