General Information
-
DRAMP ID
- DRAMP02511
-
Peptide Name
- Crotamine (defensin-like toxin; Snakes, reptiles, animals)
-
Source
- Crotalus durissus terrificus (South American rattlesnake)
-
Family
- Belongs to the crotamine-myotoxin family
-
Gene
- CRO2
-
Sequence
- YKQCHKKGGHCFPKEKICLPPSSDFGKMDCRWRWKCCKKGSG
-
Sequence Length
- 42
-
UniProt Entry
- Q9PWF3
-
Protein Existence
- Protein level
Activity Information
-
Biological Activity
- Antimicrobial, Antibacterial, Anti-Gram+, Anti-Gram-, Cytotoxic, Antifungal
-
Target Organism
-
- [Swiss_Prot Entry Q9PWF3]Gram-positive bacterium: Staphylococcus aureus;
- Gram-negative bacteria: Escherichia coli;
- Yeast: Candida albicans
-
Hemolytic Activity
-
- [Ref.210622]Non-hemolytic activity
-
Cytotoxicity
-
- Not included yet
-
Binding Target
- Eukaryotic ion channels
Structure Information
-
Linear/Cyclic
- Not included yet
-
N-terminal Modification
- Not included yet
-
C-terminal Modification
- Not included yet
-
Nonterminal Modifications and Unusual Amino Acids
- Not included yet
-
Stereochemistry
- Not included yet
-
Structure
- Combine helix and strand structure
-
Structure Description
- Crotamine contains an alpha-helix with residues 1-7 and a two-stranded anti-parallel beta-sheet with residues 9-13 and 34-38 as the only regular secondary structures. These are connected with each other and the remainder of the polypeptide chain by the three disulfide bonds, which also form part of a central hydrophobic core (Ref.2).
-
Helical Wheel Diagram
-
PDB ID
- 1Z99 resolved by NMR.
-
Predicted Structure
- There is no predicted structure for DRAMP02511.
Physicochemical Information
-
Formula
- C214H332N64O54S7
Absent Amino Acids
- ANTV
Common Amino Acids
- K
Mass
- 4889.81
PI
- 9.51
Basic Residues
- 13
Acidic Residues
- 3
Hydrophobic Residues
- 6
Net Charge
- +10
-
Boman Index
- -94.05
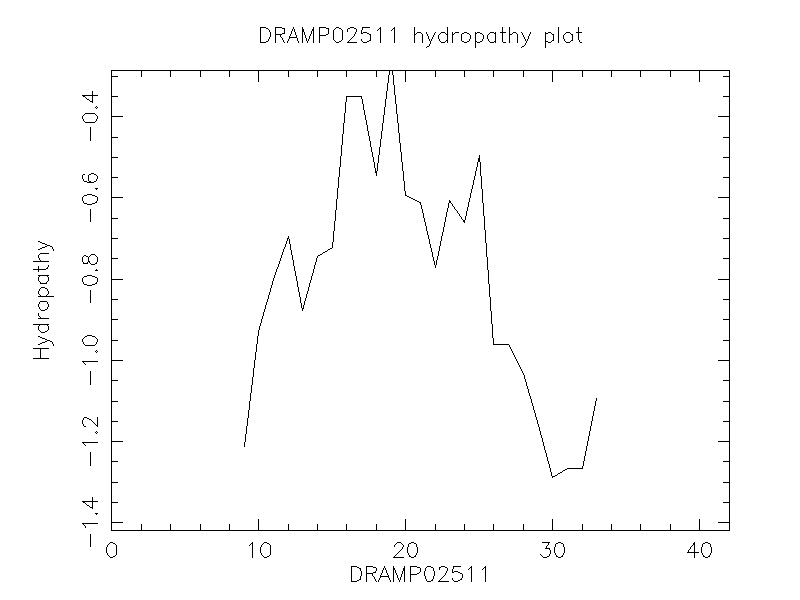
Hydrophobicity
- -1.095
Aliphatic Index
- 18.57
Half Life
-
- Mammalian:2.8 hour
- Yeast:10 min
- E.coli:2 min
Extinction Coefficient Cystines
- 12865
Absorbance 280nm
- 313.78
Polar Residues
- 15
DRAMP02511
Comments Information
Function
- It exhibits antimicrobial activities, hind limb paralysis, and severe muscle necrosis by a non-enzymatic mechanism. As a cell-penetrating peptide, crotamine has high specificity for actively proliferating cells, and interacts inside the cell with subcellular and subnuclear structures, like vesicular compartments, chromosomes and centrioles. Crotamine has marked activity against the eukaryotic pathogen Candida albicans at pH 7.5 or 5.5.
Tissue specificity
- Expressed by the venom gland.
Toxic dose
- LD50 is 1.5 mg/kg by intravenous injection. LD50 is 32.8 mg/kg by intraperitoneal injection into mice.(Ref.3)(Ref.4)
Pharmaceutical use
- Has high potential for use as an anticancer agent. In vivo treatment with this protein significantly delays tumor implantation, inhibits tumor growth and prolongs the lifespan of the mice with melanoma tumors. It has also potent and specific toxicity against tumor cell lines of aggressive mouse and human tumors, but low cytotoxicity against non-tumoral cell lines. In addition, this protein can act as a carrier capable of delivering DNA into replicating cells with low cytotoxicity against normal proliferative cells.(Ref.5)(Ref.6)
Miscellaneous
- Has no hemolytic activity .
Literature Information
- ·Literature 1
-
Title
- Selective reciprocity in antimicrobial activity versus cytotoxicity of hBD-2 and crotamine.
-
Pubmed ID
- 19706485
-
Reference
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Sep 1;106(35):14972-14977.
-
Author
- Yount NY, Kupferwasser D, Spisni A, Dutz SM, Ramjan ZH, Sharma S, Waring AJ, Yeaman MR.
- ·Literature 2
-
Title
- Automated NMR structure determination and disulfide bond identification of the myotoxin crotamine from Crotalus durissus terrificus.
-
Pubmed ID
- 16185738
-
Reference
- Toxicon. 2005 Dec 1;46(7):759-767.
-
Author
- Fadel V, Bettendorff P, Herrmann T, de Azevedo WF Jr, Oliveira EB, Yamane T, Wüthrich K.
- ·Literature 3
-
Title
- The primary structure of crotamine (author's transl).
-
Pubmed ID
- 1176086
-
Reference
- Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Feb;356(2):213-215.
-
Author
- Laure CJ.
- ·Literature 4
-
Title
- he analgesic activity of crotamine, a neurotoxin from Crotalus durissus terrificus (South American rattlesnake) venom: a biochemical and pharmacological study.
-
Pubmed ID
- 9839677
-
Reference
- Toxicon. 1998 Dec;36(12):1927-1937.
-
Author
- Mancin AC, Soares AM, Andrião-Escarso SH, Faça VM, Greene LJ, Zuccolotto S, Pelá IR, Giglio JR.
- ·Literature 5
-
Title
- The natural cell-penetrating peptide crotamine targets tu
-
Pubmed ID
- 22142367
-
Reference
- Mol Pharm. 2012 Feb 6
-
Author
- Nascimento FD, Sancey L, Pereira A, Rome C, Oliveira V, Oliveira EB, Nader HB, Yamane T, Kerkis I, Tersariol IL, Coll JL, Hayashi MA.
- ·Literature 6
-
Title
-
Pubmed ID
- 210622
-
Reference
-
Author
- Kerkis I, Silva