General Information
-
DRAMP ID
- DRAMP03734
-
Peptide Name
- Parabutoporin (PP; Non-disulfide-bridged peptide 3.2, NDBP-3.2; Arthropods, animals)
-
Source
- Parabuthus schlechteri (Scorpion)
-
Family
- Belongs to the scorpion BPP family
-
Gene
- Not found
-
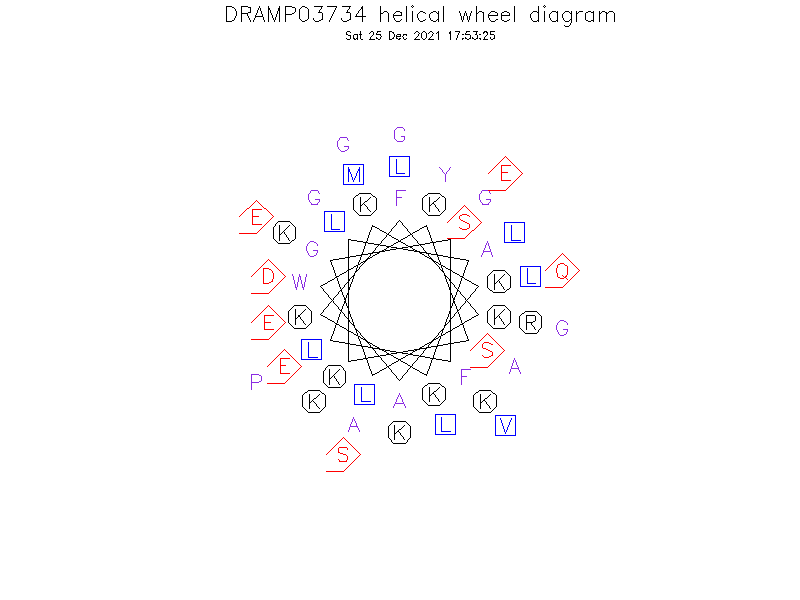
Sequence
- FKLGSFLKKAWKSKLAKKLRAKGKEMLKDYAKGLLEGGSEEVPGQ
-
Sequence Length
- 45
-
UniProt Entry
- P83312
-
Protein Existence
- Protein level
Activity Information
-
Biological Activity
- Antimicrobial, Antibacterial, Anti-Gram+, Anti-Gram-, Antifungal
-
Target Organism
-
- [Ref.12354111]Gram-negative bacteria: Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 (MIC=3.1 µM), Escherichia coli DH5a (MIC=3.1 µM), Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 257853 (MIC=6.3 µM), Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 13833 (MIC=1.6 µM), Salmonella choleraesuis ATCC 13311 (MIC=3.1 µM), Haemophilus influenzae ATCC 19418 (MIC=3.1 µM);
- Gram-positive bacteria: Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6051 (MIC=6.3 µM), Listeria monocytogenes NCTC 11994 (MIC=6.3 µM), Micrococcus luteus ATCC 9341 (MIC=25 µM);
- Fungi: Neurospora crassa (MIC=2.5 µM), Botrytis cinerea (MIC=3.5 µM), Fusarium culmorum (MIC=0.3 µM), Saccharomyces cerevisiae (MIC=2 µM).
-
Hemolytic Activity
-
- [Ref.12354111]50% hemolysis is induced by about 38 µM against human red blood cells
-
Cytotoxicity
-
- Not included yet
-
Binding Target
- Cell membrane
Structure Information
-
Linear/Cyclic
- Linear
-
N-terminal Modification
- Free
-
C-terminal Modification
- Free
-
Nonterminal Modifications and Unusual Amino Acids
- Free
-
Stereochemistry
- L
-
Structure
- Not found
-
Structure Description
- Not found
-
Helical Wheel Diagram
-
PDB ID
- None
-
Predicted Structure
- There is no predicted structure for DRAMP03734.
Physicochemical Information
-
Formula
- C229H379N61O61S
Absent Amino Acids
- CHINT
Common Amino Acids
- K
Mass
- 4994.96
PI
- 10
Basic Residues
- 12
Acidic Residues
- 5
Hydrophobic Residues
- 15
Net Charge
- +7
-
Boman Index
- -65.81
Hydrophobicity
- -0.7
Aliphatic Index
- 76
Half Life
-
- Mammalian:1.1 hour
- Yeast:3 min
- E.coli:2 min
Extinction Coefficient Cystines
- 6990
Absorbance 280nm
- 158.86
Polar Residues
- 10
DRAMP03734
Comments Information
Function
- At high concentrations, acts as pore former in cellular membranes and causes the leakage of the cells. At submicromolar concentrations, degranulates granulocytes and has hemolytic activity against human red blood cells. Also strongly inhibits the production of superoxide anions. Has a strong antibacterial activity against Gram-negative bacteria but is less active against Gram-positive bacteria. Also has antifungal activity. Induces reversible G-protein dependent Ca2+ release from intracellular stores and increase Ca2+ influx in HL-60 cells. Induces the activation of the Rac pathway in granulocytes. Synergistically enhances the excitatory effects of short and long chain ion-channel-specific neurotoxins by interaction with the neuronal membranes.
Tissue specificity
- Expressed by the venom gland.
NOTE
- residue 11, 44, 55 are uncertainty.
Literature Information
- ·Literature 1
-
Title
- Antibacterial and antifungal properties of alpha-helical, cationic peptides in the venom of scorpions from southern Africa.
-
Pubmed ID
- 12354111
-
Reference
- Eur J Biochem. 2002 Oct;269(19):4799-4810.
-
Author
- Moerman L, Bosteels S, Noppe W, Willems J, Clynen E, Schoofs L, Thevissen K, Tytgat J, Van Eldere J, Van Der Walt J, Verdonck F.Willems J, Noppe W, Moerman L, van der Walt J, Verdonck F.
- ·Literature 2
-
Title
- Cationic peptides from scorpion venom can stimulate and inhibit polymorphonuclear granulocytes.
-
Pubmed ID
- 12457879
-
Reference
- Toxicon. 2002 Dec;40(12):1679-1683.
-
Author
- Moerman L, Verdonck F, Willems J, Tytgat J, Bosteels S.
- ·Literature 3
-
Title
- Antimicrobial peptides from scorpion venom induce Ca(2+) signaling in HL-60 cells.
-
Pubmed ID
- 14575699
-
Reference
- iochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003 Nov 7;311(1):90-97.
-
Author
- Willems J, Moerman L, Bosteels S, Bruyneel E, Ryniers F, Verdonck F.
- ·Literature 4
-
Title
- Parabutoporin--an antibiotic peptide from scorpion venom--can both induce activation and inhibition of granulocyte cell functions.
-
Pubmed ID
- 15245865
-
Reference
- Peptides. 2004 Jul;25(7):1079-1084.
-
Author