General Information
-
DRAMP ID
- DRAMP18194
-
Peptide Name
- AAEL000598-PA
-
Source
- Aedes aegypti (Yellowfever mosquito) (Culex aegypti)
-
Family
- Not found
-
Gene
- CECD
-
Sequence
- GGLKKLGKKLEGAGKRVFKASEKALPVVVGIKAIGK
-
Sequence Length
- 36
-
UniProt Entry
- Q17NR1
-
Protein Existence
Activity Information
-
Biological Activity
- Antimicrobial, Antibacterial, Anti-Gram+, Anti-Gram-
-
Target Organism
-
- Gram-negative (including drug-resistent): E. coli (MIC 2-4 ug/mL), P. aeruginosa (MIC 1-4 ug/mL), A. baumannii (MIC 1-2 ug/mL), K. pneunomiae (MIC 1-2 ug/mL).
- No antibacterial effects of the peptide were observed against different isolates of Gram-positive S. aureus, E. faecalis and E. faecium strains showing MIC values over 32. (Pubmed: 25162372)
-
Hemolytic Activity
-
- No hemolysis information or data found in the reference(s) presented in this entry
-
Cytotoxicity
-
- Not included yet
-
Binding Target
- Not found
Structure Information
-
Linear/Cyclic
- Not included yet
-
N-terminal Modification
- Not included yet
-
C-terminal Modification
- Not included yet
-
Nonterminal Modifications and Unusual Amino Acids
- Not included yet
-
Stereochemistry
- Not included yet
-
Structure
- alpha helical (N-terminal)
-
Structure Description
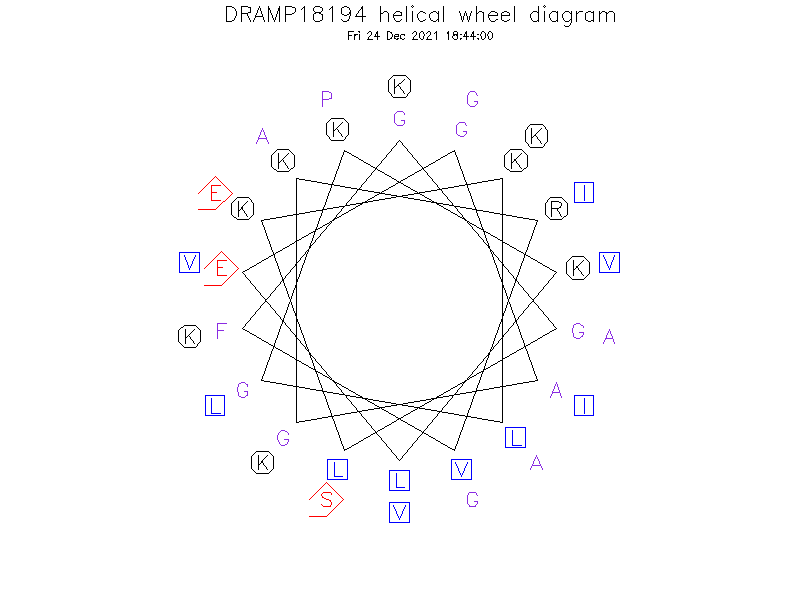
- The structure of Aedesin is depicted as a helix-bent-helix structure with good RMSD statistics for the N-terminal helix (helix 1) and for the C-terminal helix (helix 2) taken separately.The helical wheel diagram of Aedesin shows the amphipathic character of the first and second aloha helices, as well as the opposite localization of their hydrophobic and positively charged residues, respectively.
-
Helical Wheel Diagram
-
PDB ID
- 2MMM resolved by NMR.
-
Predicted Structure
- There is no predicted structure for DRAMP18194.
Physicochemical Information
-
Formula
- C169H300N48O42
Absent Amino Acids
- CDHMNQTWY
Common Amino Acids
- K
Mass
- 3676.54
PI
- 10.54
Basic Residues
- 10
Acidic Residues
- 2
Hydrophobic Residues
- 15
Net Charge
- +8
-
Boman Index
- -1941
Hydrophobicity
- -0.022
Aliphatic Index
- 108.33
Half Life
-
- Mammalian:30 hour
- Yeast:>20 hour
- E.coli:>10 hour
Extinction Coefficient Cystines
- 0
Absorbance 280nm
- 0
Polar Residues
- 8
DRAMP18194
Comments Information
The anti-bacterial activity of Aedesin was found to be salt-resistant, indicating that it is active under physiological conditions encountered in body fluids characterized by ionic salt concentrations.
Literature Information
- ·Literature 1
-
Title
- Genome sequence of Aedes aegypti, a major arbovirus vector.
-
Pubmed ID
- 17510324
-
Reference
- Science 316:1718-1723(2007).
-
Author
- Nene V., Wortman J.R., Lawson D., et al.
- ·Literature 2
-
Title
- Aedesin: structure and antimicrobial activity against multidrugresistant bacterial strains.
-
Pubmed ID
- 25162372
-
Reference
- PLoS ONE 9:e105441-e105441(2014).
-
Author
- Godreuil S., Leban N., Padilla A., et al.